Sustainability Due Diligence
Australian parliaments – supported by decisions of the High Court – have been encouraging the adoption of due diligence as a general concept to be applied throughout Australian society.
For example, due diligence in legislation is now called up by the Corporations Act (Cth) legislation, environmental legislation (e.g. NSW and Vic), model WHS legislation and Rail Safety National law etc.
In addition, earlier decisions of the High Court have been endorsed the idea. For example, the judges of the High Court unanimously agreed with the NSW Court of Appeal in 1980 [1] that due diligence as called up in the Hague Rules (to which Australia is a signatory) meant due care against negligence.
Due diligence is a legal concept. It represents an aspect of moral philosophy, that is, how the world ought to be and how humanity should behave in order to bring this about.
In practice, it seems to be an implementation of the ethic of reciprocity, often referred to as the Golden Rule in most philosophies and religions. Essentially, this means treat others as you would expect to be treated by them, or, do unto others as you would have done unto you. At least, that is what Lord Atkin indicated in Donaghue vs Stevenson (1932) [2].
In court this seems to be often tested (with the benefit of hindsight) in the form of the reasonable man test, meaning what would a reasonable man have done in the same circumstances. This is a complex idea as an American law professor notes [3]:
"The reasonable person is not any particular person or an average person… The reasonable person looks before he leaps, never pets a strange dog, waits for the airplane to come to a complete stop at the gate before unbuckling his seatbelt, and otherwise engages in the type of cautious conduct that annoys the rest of us… “This excellent but odious character stands like a monument in our courts of justice, vainly appealing to his fellow citizens to order their lives after his own example."
Much of all this is summarised in the Engineers Australia Safety Case Guideline (3rd edition), which is being launched at the National Convention in Melbourne this month. But what does all this mean and where are we heading, at least as engineers?
As something of an intellectual exercise, an attempt to apply the anticipated requirements (the logical consequence set) of recent Australian legislation and the common law decisions to date as they might be applied to global warming was presented last month by the authors at the NSW Regional Engineers Sustainability conference in Wollongong [4].
Our courts and parliaments require that, when it comes to the examination of human harm post event, all reasonable practicable precautions are demonstrated as being in place at the time decisions were made. To achieve this requires a number of steps.
The key steps for a due diligence argument are:
- A completeness argument as to why all key plausible critical issues were identified
- Identification of all physically possible precautions for each plausible critical issue
- Identification of which precautions in the circumstances are reasonable, balancing the significance of the risk vs. the effort required to achieve it (cost, difficulty and inconvenience and whatever other conflicting responsibilities the defendant may have).
Based on CSIRO studies, it does seem that the planet is warming. Whether this is entirely due to human activity (greenhouse gas emissions) or natural forces is argued extensively, but there does seem to be general agreement that for the 6 billion people on planet Earth, more than two degrees Celsius is problematic. After that, no one’s too sure what might come next. A runaway temperature change that melts the three-kilometre deep Greenland ice sheet [5], for example, will result in a seven metre increase in sea levels, with dire consequences for low lying seaboard cities like Melbourne. This certainly seems a plausible, critical scenario and one that Australian governments should be seen to consider carefully.
Many options are being discussed to address the issue, including controlling carbon emissions, which has proved politically difficult and - if the planet is naturally warming - ineffective. A recent remarkable claim by Lockheed Martin’s “Skunkworks” that fusion energy is only five years [6] away would certainly address this.
There are, however, a number of other, apparently viable precautions of differing costs and effectiveness. The Krakatoa explosion [7] of 1883 apparently cooled the planet by about 1.2o degrees Celsius for a year as a result of the increased albedo effect (reflecting sunlight back in to space). We don’t yet seem to be able to predict such events in advance, so cooling the planet by that means would seem to more a matter of good luck than good governance.
Such precautions can be summarised in a threat-barrier diagram (TBD):
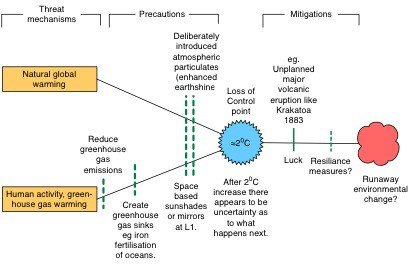
Central to a TBD is the loss of control (LoC) point. This is the point at which the laws of nature and man align. Legally, precautions act before the LoC whilst mitigations act after it.
There are a number of possible options available that would achieve a similar effect to a Krakatoa 1883 explosion, including pumping moisture into the air [8] to produce more reflective white clouds.
Sun shields such as the La Grangian L1 point between the Earth and the sun [9] would be effective too. Another method, possibly the cheapest and most effective of the lot, seems to be the fertilisation of the Southern Ocean [10] to create carbon absorbing algal blooms which would both cool the planet and act as a carbon sink, thereby de-acidifying the oceans.
According to Treasury [11], the Victorian desalination plant has presently cost the Victorian taxpayer $5.7 billion despite the fact that no water has been purchased. The reason for the plant's construction seems to based on a due diligence argument.
At the time of the decision, much of Australia had experienced a 10-year drought. If this had continued for another 10 years, the possibility of a major Australian population centre running out of water was deemed quite plausible. As state cabinet had the means within its power to ensure that this could not happen, it was done, even if it more likely than not will never be needed.

$5.7 billion is a lot of money. Many of the ideas mentioned to address global warming apparently could be implemented for such a sum. If so, it would appear to be within the power of the Victorian parliament and society to prevent a plausible catastrophic flooding of Melbourne due to runaway global warming.
Provided the science and numbers are right (and it is crucial that this be verified and validated), a perpetuation of the due diligence approach would seem to require the Victorian parliament to investigate and potentially act to protect Melbourne – and incidentally cool the whole planet.
References:
[1] Shipping Corporation of India Ltd. v. Gamlen Chemical Co. A/Asia. Pty. Ltd. [1980] HCA 51; (1980) 147 CLR 142
[2] See http://www.bailii.org/uk/cases/UKHL/1932/100.html viewed 17 July 2013
[3] J M Feinman (2010). Law 101. Everything You Need to Know About American Law. Oxford University Press. Page 159
[4] See http://www.engineersaustralia.org.au/events/nsw-regional-convention-sustainable-regional-engineering
[5] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greenland_ice_sheet viewed 7nov14
[6] http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/health-science/lockheed-martin-unveils-miniature-nuclear-fusion-power-generator/story-e6frg8y6-1227092587574?nk=4536f2c5e9e39c3c7dd336b0aae01f5c viewed 7nov14
[7] See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1883_eruption_of_Krakatoa viewed 7nov14.
[8] See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:SPICE_TESTBED_-_DEPLOYED_POSITION.jpg#filehistory viewed 7nov14, for an example.
[9] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_sunshade viewed 7nov14.
[10] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ocean_fertilization and http://www.acecrc.org.au/Research/Ocean%20Fertilisation and http://marineecology.wcp.muohio.edu/climate_projects_04/productivity/web/ironfert.html viewed 3nov14
[11] http://www.dtf.vic.gov.au/Infrastructure-Delivery/Public-private-partnerships/Projects/Victorian-Desalination-Plant viewed 3nov14.
This article first appeared on Sourceable.
Safety in Design - A Due Diligence Perspective
Due diligence is a legal concept. From the Concise Australian Legal Dictionary, due diligence is, a minimum standard of behaviour involving a system which provides against contravention of relevant regulatory provisions and adequate supervision ensuring that the system is properly carried out. The concept of due diligence has been captured in Corporations law, Environmental Law and now the model Work Health and Safety legislation.In an engineering and technological context due diligence is often construed to just mean compliance. This is not the case.Due diligence is an aspect of moral philosophy, that is how the world ought to be and how humanity ought to behave to achieve it. Often, this is along the lines that one should treat others as you would like to be treated by them.Due diligence for safety in design purposes uses the principles behind the judgments of the courts and applies them pre-event to ensure sound decision making. That is, reverse engineering of judicial decisions as shown above.How this manifests itself is that sometimes bad things happen and Courts and Royal Commissions question the design and design process with the advantage of hindsight to see what could have been in place, if it had been in place would have stopped the bad thing / accident from happening. Outcomes from such investigations are then fed back to see if the parties involved in the design were diligent.Safety due diligence is all about showing pre-event that the operation is safe. This means that when safety is being considered in the design process, all of the people that could be affected by the design need to be taken into account and the potential hazards to which they are exposed, over the entire lifecycle.From a safety due diligence aspect, all reasonable practicable precautions need to be in place applying the hierarchy of controls.
Demonstrating Societal Due Diligence Using the Precautionary Approach
Arising from correspondence and discussion regarding earthquakes in New Zealand and bushfires in Victoria, R2A has been considering the possible application of the precautionary approach from a government regulatory perspective. The Venn diagram below is one result.
Arising from correspondence and discussion regarding earthquakes in New Zealand and bushfires in Victoria, R2A has been considering the possible application of the precautionary approach from a government regulatory perspective. The Venn diagram below is one result.
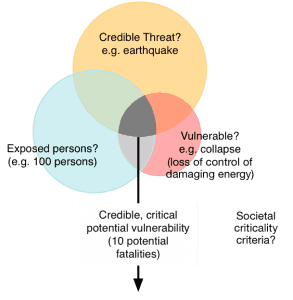
This implies three primary control options: eliminate the threat, remove exposed persons, or reduce the vulnerability. All are viable options with different perspectives but typically fall into different ‘control’ domains. For example, the ‘exposed persons’ issue is usually a land use planning matter generally being the responsibility of local government. The issue of vulnerability is usually an engineering concern the responsibility for which mostly falls to owners of exposed facilities. The nature of the threat is more a scientific matter and typically the concern of research organisations.
This makes the grey intersection a complex disciplinary patch, with overlapping responsibilities for government agencies, research and engineering organisations and with all the confusions as to whether the ‘hazard’ is a personal problem and the responsibility of individual owners, or a societal problem to be addressed with community resources.
Perhaps the most useful observation from this model to date is that the elimination of persons from an exposed area, a quite natural government response, is only one of three possibilities. The model above suggests that the optimal societal course of action is likely to be a mixture of the three control domains.
